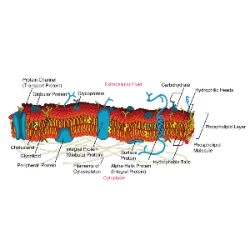
Enzyme Inhibition and Metabolic Regulation
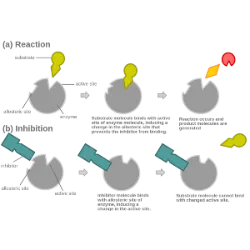
Enzyme inhibition is a fundamental process in the regulation of metabolic activities, allowing the organism to control biochemical reactions in a precise manner. There are two main types of enzyme inhibition: competitive and non-competitive. In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme, competing with the substrate and decreasing the reaction rate. In non-competitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds to another site of the enzyme, altering its structure and decreasing catalytic efficiency, even if the substrate is present.
In addition, enzymes can be regulated by negative and positive feedback mechanisms. In negative feedback, the end product of an enzymatic reaction inhibits the enzyme that catalyzes the initial reaction, preventing the excessive production of a compound. This mechanism is crucial for maintaining homeostatic balance in the organism. On the other hand, positive feedback increases enzymatic activity, accelerating the production of products in certain situations, such as blood clotting.
These metabolic inhibition and regulation processes are essential for the body's adaptation to changes in internal and external conditions, ensuring that metabolism occurs efficiently and in a controlled manner.
Did you know?