Reproductive System
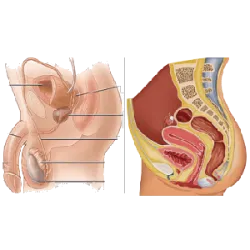
It is responsible for reproduction, ensuring the perpetuation of the species through the formation of gametes (sex cells) and fertilization.
Male Reproductive System:
Produces sperm (male gametes).
Main bodies:
Testicles: Produce sperm and testosterone.
Penis: Copulatory organ.
Prostate and Seminal Vesicles: Produce fluids that make up semen.
Female Reproductive System:
Main bodies:
Ovaries: Produce eggs and hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
Uterus: Place where the embryo develops.
Vagina: Channel that connects the outside to the uterus.
Examples of processes in the reproductive system:
Ovulation: Release of an egg from the ovaries.
Fertilization: Union of sperm and egg.
Pregnancy: Development of the embryo in the uterus.
The reproductive system is essential for the continuity of life and works in interaction with other systems, such as the endocrine system.
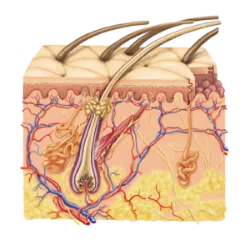
Its function is to detect, process and respond to environmental stimuli
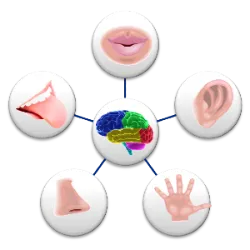
Its function is to detect, process and respond to environmental stimuli, ensuring perception and interaction with the external and internal world.
Features:
Made up of sense organs (vision, hearing, touch, smell, taste).
It connects to the nervous system to transmit information to the brain.
Responds to physical, chemical and thermal stimuli.
Bodies and examples:
Vision (Eyes): Detect light and images (e.g. retina).
Hearing (Ears): Capture sounds and help with balance (e.g. cochlea).
Touch (Skin): Feels pressure, temperature and pain (e.g.: nerve endings).
Smell (Nose): Identifies odors (e.g.: olfactory bulb).
Taste (Language): Recognizes flavors (e.g. taste buds).
The sensory system allows us to explore and understand the world, adapting to different environments.
Test yourself with one of these challenges 👇
Discover some interesting facts about Human Body Systems
Excretory System
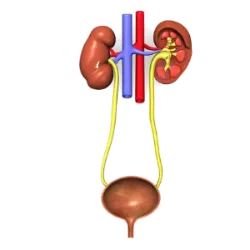
They have the function of eliminating metabolic waste from the body (such as urea and carbon dioxide) and maintaining the body's water and chemical balance.
Composition and Characteristics:
Kidneys: Filter the blood, forming urine.
Ureters: Conduct urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Bladder: Stores urine.
Urethra: Eliminates urine out.
Regulates the volume of liquids, electrolytes and blood pH.
It works together with other systems, such as the circulatory system.
Examples of processes:
Filtration: Occurs in the nephrons of the kidneys.
Urine formation: Excretion of substances such as urea, salts and water.
Waste elimination: Through urination.
The excretory system is essential for detoxifying the body and maintaining internal balance (homeostasis).
Locomotor System

Its function is to allow movement, support the body, protect internal organs and interact with the environment.
Composition:
Skeletal System: Bones and joints.
Muscular System: Muscles that promote movement.
It works in an integrated way: muscles contract and bones serve as levers.
Provides posture, balance and mobility.
Examples of components:
Bones: Femur (support), skull (protection).
Muscles: Biceps (arm movement), quadriceps (locomotion).
Joints: Knee, shoulder (facilitate movement).
The locomotor system is essential for daily activities such as walking, running and lifting objects.
Endocrine System
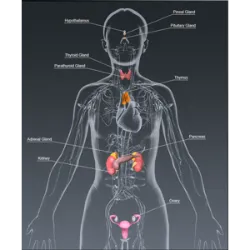
Their function is to produce and release hormones that regulate various body functions, such as growth, metabolism, reproduction and internal balance (homeostasis).
Features:
Formed by endocrine glands, which release hormones directly into the blood.
It acts slowly but lastingly, regulating bodily processes.
Works together with the nervous system to maintain balance in the body.
Main Glands and Hormones:
Pituitary gland (master gland): Controls other glands and produces hormones such as GH (growth).
Thyroid: Regulates metabolism (T3 and T4 hormones).
Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon (glucose control).
Adrenals: Release adrenaline and cortisol (stress response).
Ovaries and Testicles: Produce sexual hormones (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone).
The endocrine system is essential for maintaining the body's harmony, regulating vital functions continuously and precisely.
Its function is to control and coordinate all body functions
Its function is to control and coordinate all body functions, processing stimuli from the environment and generating quick responses.
Main Divisions and Resources:
Central Nervous System (CNS): Formed by the brain and spinal cord, processes information.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves that connect the body to the CNS.
It acts through electrical impulses and neurotransmitters.
Regulates voluntary (movements) and involuntary (heartbeat) actions.
Main components:
Brain: Controls thought, memory, and senses.
Spinal cord: Conducts signals between the brain and the body.
Nerves: Transmit nerve impulses.
Neurons: Cells that process and transmit information.
The nervous system is essential for understanding the environment, making decisions and keeping the body functioning in an integrated way.
Lymphatic System
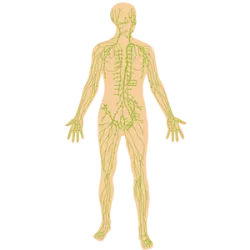
Its function is to transport liquids (lymph), fats and immune cells. Remove waste and maintain fluid balance in the body.
Features:
Composed of lymphatic vessels, lymph, lymph nodes and organs (spleen, thymus).
Works together with the circulatory system.
Filters microorganisms and toxins from body tissues.
Examples of components:
Lymph: Liquid that transports white blood cells.
Lymph nodes: "Filters" that fight infections.
Spleen: Produces and destroys old blood cells.
Thymus: Matures T lymphocytes (immune cells).
Test yourself with one of these challenges 👇
HOME