The Pathways of Cellular Metabolism
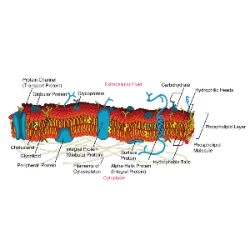
Energy production in cells depends on three fundamental processes: glycolysis, Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain. These mechanisms ensure the conversion of nutrients into ATP, the main source of cellular energy.
Glycolysis, the first stage, occurs in the cytoplasm and breaks down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate molecules, generating ATP and NADH. If oxygen is available, the pyruvate goes to the mitochondria, where the Krebs Cycle occurs. In this phase, acetyl-CoA molecules are processed, releasing CO₂ and producing more NADH and FADH₂, electron transporters.
The last stage is the Electron Transport Chain, located in the mitochondrial membrane. In it, electrons pass through specialized proteins, generating a proton gradient that drives the synthesis of ATP. This process ends cellular respiration and ensures the greatest energy production in the organism.
Did you know?