French Revolution (1789-1799)
The French Revolution, which began in 1789, was a historic event that profoundly transformed France and had a global impact. The financial crisis, aggravated by the public debt and excessive spending by the monarchy, led to severe food shortages and popular discontent. The nobility and the clergy maintained their privileges, while the Third Estate (peasants, bourgeoisie and urban workers) suffered from high taxes and economic hardship.
The movement began with the convocation of the Estates General, where the Third Estate rebelled and formed the National Assembly. On 14 July 1789, the fall of the Bastille symbolized the beginning of the struggle against absolutism. In 1791, France proclaimed the Constitution and became a constitutional monarchy.
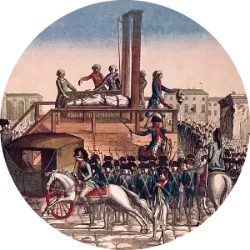
However, the regime of Louis XVI was unable to sustain itself. In 1792, the monarchy was abolished and the Republic was proclaimed. The Revolution entered a radical phase with the rise of the Jacobins and the execution of the king. During the Reign of Terror (1793–1794), thousands of opponents were executed, including figures such as Robespierre.
The Revolution culminated in the coup of 1799, when Napoleon Bonaparte took power, ending the revolutionary period and ushering in the Empire.
Did you know?