Cardiovascular System
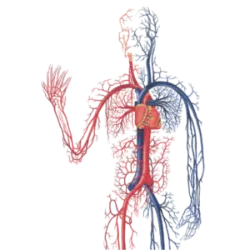
Its main function is to transport blood, nutrients, oxygen and waste throughout the body, as well as regulate temperature and maintain fluid balance.
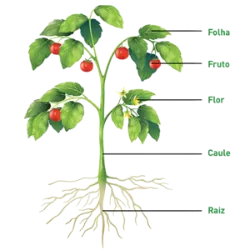
Components:
Heart: Pumps blood.
Divided into four chambers (two atria and two ventricles).
The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the body.
The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
Blood vessels: Arteries (take blood from the heart to the body), veins (return blood to the heart), and capillaries (exchange gases and nutrients with tissues).
Blood: Composed of plasma, red blood cells (oxygen transport), white blood cells (defense) and platelets (coagulation).
Circulation:
Pulmonary: Blood goes from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Systemic: Oxygenated blood goes from the heart to the body.
Closed system: Blood constantly circulates within the vessels, without leaving the external environment.
Did you know?