Endocrine System
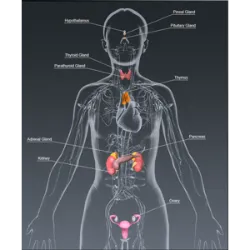
Their function is to produce and release hormones that regulate various body functions, such as growth, metabolism, reproduction and internal balance (homeostasis).
Features:
Formed by endocrine glands, which release hormones directly into the blood.
It acts slowly but lastingly, regulating bodily processes.
Works together with the nervous system to maintain balance in the body.
Main Glands and Hormones:
Pituitary gland (master gland): Controls other glands and produces hormones such as GH (growth).
Thyroid: Regulates metabolism (T3 and T4 hormones).
Pancreas: Produces insulin and glucagon (glucose control).
Adrenals: Release adrenaline and cortisol (stress response).
Ovaries and Testicles: Produce sexual hormones (estrogen, progesterone, testosterone).
The endocrine system is essential for maintaining the body's harmony, regulating vital functions continuously and precisely.
Did you know?