The Rise of Greek Civilization
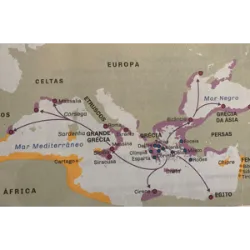
Greece is located on the Balkan Peninsula and is washed by the Mediterranean Sea. Its civilization emerged from the 8th century BC, having its roots in mainland Greece, the islands of the Aegean Sea and the coasts of Asia Minor. It later expanded to the shores of the Mediterranean Sea, establishing colonies that contributed to economic and cultural links.
April 25 is the day of the Carnation Revolution

April 25 is the day of the Carnation Revolution, a historic event in Portugal that took place on April 25, 1974, which overthrew the dictatorial regime of the Estado Novo, in power since 1933. Led by the Armed Forces Movement (MFA), composed mainly of captains who had participated in the Colonial War, the movement had massive popular support. The military action resulted in few civilian casualties and led to the appointment of the Junta de Salvação Nacional to govern the country. A period of social and political unrest known as PREC (Ongoing Revolutionary Process) followed. On April 25, 1976, a new democratic Constitution came into force, marking the end of the authoritarian regime and the beginning of a democratic period in Portugal. The military coup was triggered by dissatisfaction with the colonial war, internal divisions within the regime and political repression.
Test yourself with one of these challenges 👇
Discover some interesting facts about Academic
The Origin of the Conditions for Life

Some important events in Earth's history that created the conditions for the emergence of life over thousands of years include: the formation of the planet with impacts from other bodies in the Solar System; the creation of a solid crust, with continents and oceans; the development of an atmosphere with a greenhouse effect; the movement of tectonic plates and volcanic activity; atmospheric electrical phenomena; the formation of simple organic molecules and macromolecules; the emergence of the first primitive cells; the beginning of photosynthesis and the production of oxygen; the creation of the ozone layer and superglaciations that gave rise to new environments.
Molar mass

Molar mass is a physical property that indicates the mass of a substance on a molecular scale. It is calculated by adding up the atomic masses of all the atoms present in a molecule or chemical formula. The unit of measurement for molar mass is grams per mole (g/mol). This unit indicates how many grams of a substance are present in 1 mole of that substance. For example, if the molar mass of a substance is 32 g/mol, that means that 1 mol of that substance weighs 32 grams. To calculate the molar mass of a substance, you need to know the atomic masses of the elements that make it up. The atomic mass of an element is found on the periodic table of elements. It represents the weighted average of the masses of the isotopes of that element.
Chemical radioactivity

Chemical radioactivity is a phenomenon in which unstable atoms emit subatomic particles or electromagnetic radiation to achieve greater nuclear stability. There are three main types of radiation: alpha particles, beta particles and gamma radiation.Alpha (α) particles: These are helium nuclei composed of two protons and two neutrons. They have a positive charge and limited penetration. Beta particles (β): These are high energy electrons or positrons. They have a lower charge and mass than alpha particles and have a greater penetration capacity. Gamma radiation (γ): It is a form of electromagnetic radiation without charge and mass. It is highly energetic and has the greatest penetrating ability. Radioactivity occurs in unstable atoms known as radioactive isotopes, which are transformed into more stable isotopes through radioactive decay. Alpha decay (α), Beta decay (β) and Gamma radiation emission (γ).
Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies organic compounds

Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies organic compounds, which contain carbon in their molecular structure. These compounds are present in nature and in synthetic products manufactured by humans. Organic chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, synthesis and reactivity of organic compounds. Structural formulas and functional groups are used to represent and identify the compounds. Topics covered include nomenclature, structure and properties, organic synthesis, reaction mechanisms and reactivity of functional groups. Organic chemistry is essential in many industrial sectors such as pharmaceuticals, polymers, food, energy and general chemicals. Its development contributes to society and science.
A quadratic equation, or quadratic equation

A quadratic equation, or quadratic equation, is a polynomial equation with the highest degree equal to 2. It is represented in the general form: ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are constants and x is the variable unknown. There are three possible types of solutions for a quadratic equation: Two real and distinct roots: When the discriminant (∆) of the equation is greater than zero (∆ > 0), the equation has two different real roots. Two real and equal roots: When the discriminant is equal to zero (∆ = 0), the equation has two real roots that are equal, resulting in a unique solution.No real roots: When the discriminant is less than zero (∆ < 0 ), the equation has no real roots. In this case, the roots can be complex conjugate numbers.
Test yourself with one of these challenges 👇
HOME














