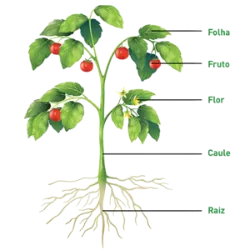
Connective Tissue
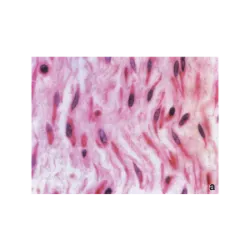
It has functions of support, filling, protection, transport of substances (such as blood), energy storage (adipose tissue) and immunological defense.
Features:
Spaced cells: Separated by an abundant extracellular matrix.
Extracellular matrix: Contains fibers (collagenous, elastic or reticular) and ground substance.
Vascularization: Generally well vascularized, except in cartilage.
Classification:
Connective tissue proper:
Loose: Fibers that are poorly organized, filling and support (e.g. dermis).
Dense: Rich in fibers, greater resistance (e.g. tendons).
Specialized:
Adipose: Stores fat and energy.
Cartilaginous: Support and flexibility (e.g. joints).
Bone: Support, protection and storage of calcium.
Blood: Transport of nutrients, gases and defense.
Hematopoietic: Production of blood cells (e.g. bone marrow).
Did you know?