Analyzing and understanding the landscape can be done

Analyzing and understanding the landscape can be done through direct observation (visualizing the phenomenon on site) or indirect observation (studying the phenomenon through written, visual, informative documents, etc.). This process requires skill in organizing information, and geographers often use landscape sketching as a technique to schematize information into three observation planes, facilitating the description of the landscape.
3rd Plane: Corresponds to the most distant part of the observer. Natural elements such as the Black Sea and the sky. Human elements: none.
2nd Plane: Located in the middle portion of the landscape. Natural elements: Black Sea and hill. Human elements: houses.
1st Plane: Closer to the observer, providing a more detailed view. It includes natural elements such as the Black Sea, vegetation and cliffs, along with human elements such as houses and a bridge.
Geography is a very old science, and was born in Greece

Geography is a very old science, and was born in Greece, at first it was limited to describing the Earth's surface known at the time.
Geography = Geo (Earth) + spelling (description)
Currently, and taking into account the complexity of the aspects that can be observed on the earth's surface, Geography is not limited to describing but also interpreting existing phenomena, as well as the relationships that are established, in order to find solutions to existing problems. In short, Geography is the science dedicated to the study of physical and human phenomena that occur on the Earth's surface and the interrelationships that they establish.
Test yourself with one of these challenges 👇
Discover some interesting facts about Landscapes and Maps
Geography

Geography is a science that studies the understanding and location of phenomena around humans, addressing the consequences of human activity in nature. Geographers use various sources of information, such as: maps, statistics, texts, photographs, films, documentaries, interviews and research, and four-step study methods to analyze geographic phenomena and find solutions for better coexistence between humans and nature:#NL #
1st stage: Observation (direct or indirect) - answers the question WHAT? (What am I observing?)
2nd stage: Location (exact location of the phenomenon) - answers the question WHERE? (Where is the landscape located?)
3rd stage: Description (All information about the observed elements is presented, accurately and clearly) answers the question HOW?
4th stage: Interpretation (Explanation of the phenomenon that occurred) answers the question WHY?
Landscape arises from the interaction between different elements

Landscape arises from the interaction between different elements, whether natural or human, in a specific location, forming a unique composition. It represents an observable portion of the Earth's surface.
The elements that make up the landscape define its structure, enabling detailed analysis. Each landscape is unique and results from the influence of natural elements, such as relief, bodies of water, vegetation, and climatic characteristics (snow, rain, cloudiness, etc.), as well as interaction with human elements, such as buildings, infrastructures, roads communications (roads, motorways, railways, canals, airports, etc.), electricity poles, industries, agricultural holdings and tourist developments.
The vast diversity of landscapes on Earth, combined with human influence

The vast diversity of landscapes on Earth, combined with human influence, has considerably expanded the scope of study of Geography. To simplify, Geography was divided into two main branches:
Physical Geography: This branch focuses on the analysis of physical or natural phenomena on the Earth's surface, such as climate, relief and hydrography.
Human Geography: This branch explores topics such as economic activities, organization of space, evolution of cities and demography, focusing on the interaction between society and the environment.
Graphic Scale: represents, through a straight line segment
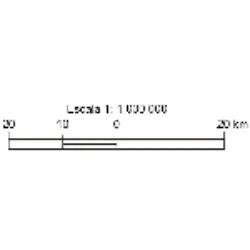
Graphic Scale: represents, through a straight line segment, the relationship between representation and reality.
It is represented by a straight line segment, divided into equal parts. Each of these divisions corresponds between actual distances and distances on the map. This scale allows quick reading of real distance values.
Advantages: We can enlarge or reduce the size of the map always maintaining the correct scale.
Landscapes, whether natural or humanized
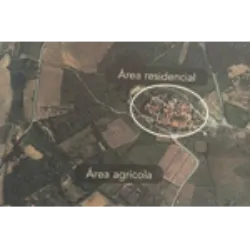
Landscapes, whether natural or humanized, are distinguished by their multifunctionality. In a rural landscape, for example, several functions are associated, such as the production of goods, conservation of resources, leisure, preservation of heritage and cultural identity, and the residential function. These functions are performed by several landscape units, which stand out from adjacent areas due to the way natural and human elements interact, and may be separate or overlapping.
Test yourself with one of these challenges 👇
HOME










